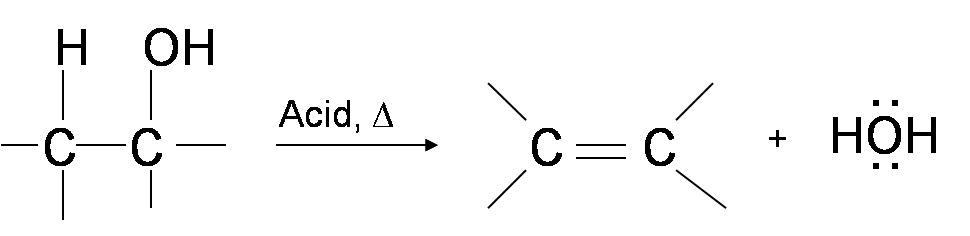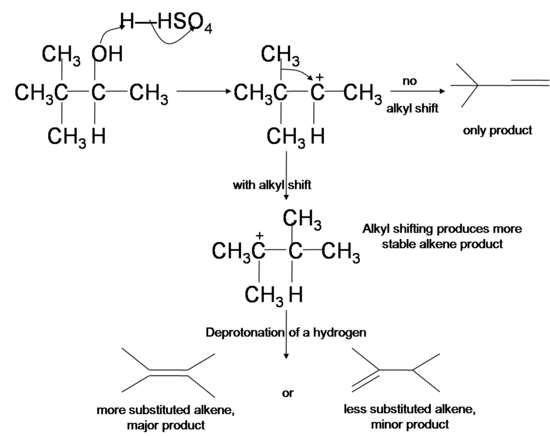Acid-Catalyzed Dehydration of Alcohols | Reaction, Mechanism & Structure - Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com

The Continuous Acid-Catalyzed Dehydration of Alcohols in Supercritical Fluids: A New Approach to the Cleaner Synthesis of Acetals, Ketals, and Ethers with High Selectivity | Journal of the American Chemical Society

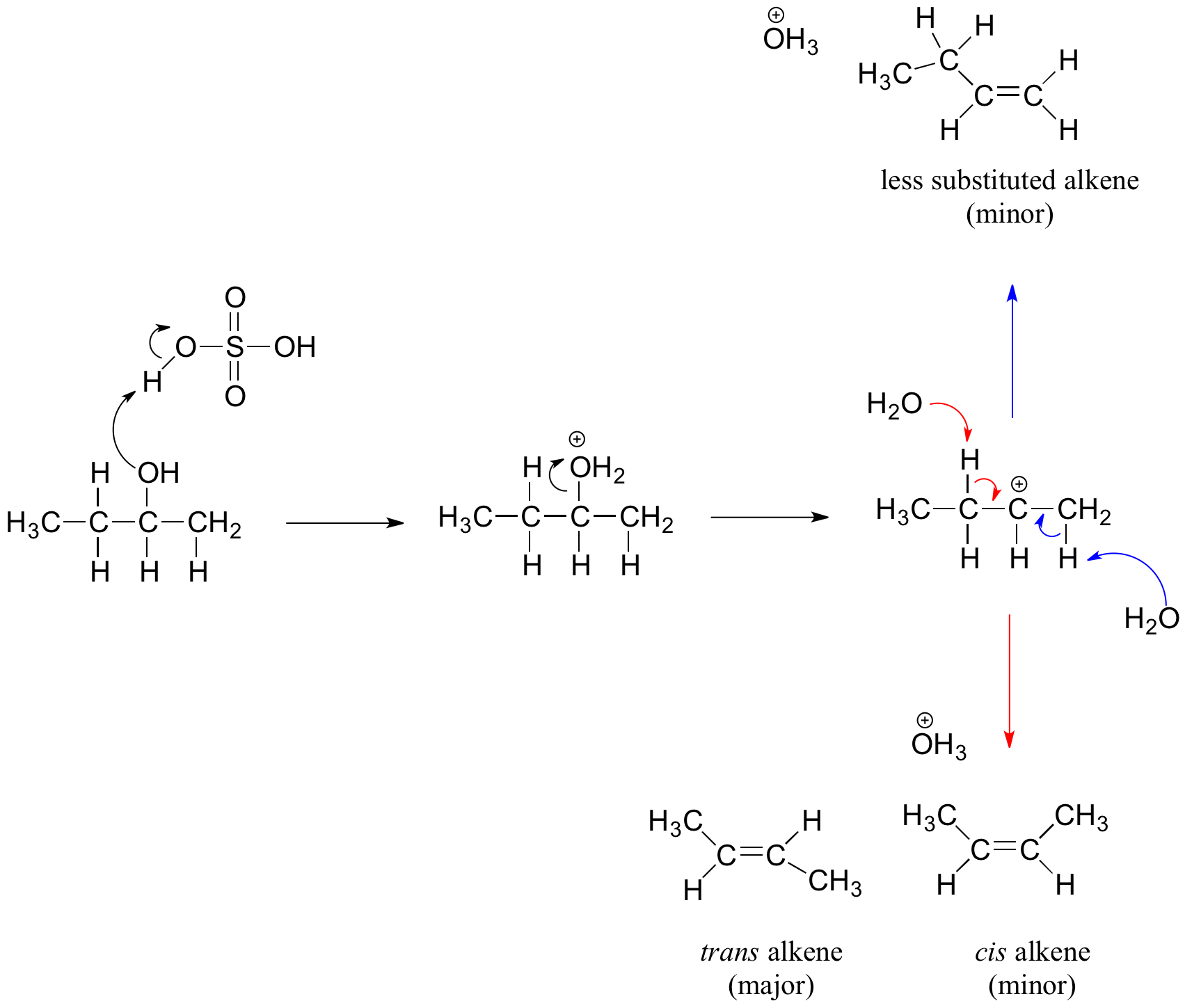
Predict the major product of acid catalysed dehydration:(i) 1 - methyl cyclohexanol(ii) Butan - 1 - ol

a) Write the mechanism of acid catalysed dehydration of ethanol to ethene.b) Between phenol and alcohol which is more acidic? Why?

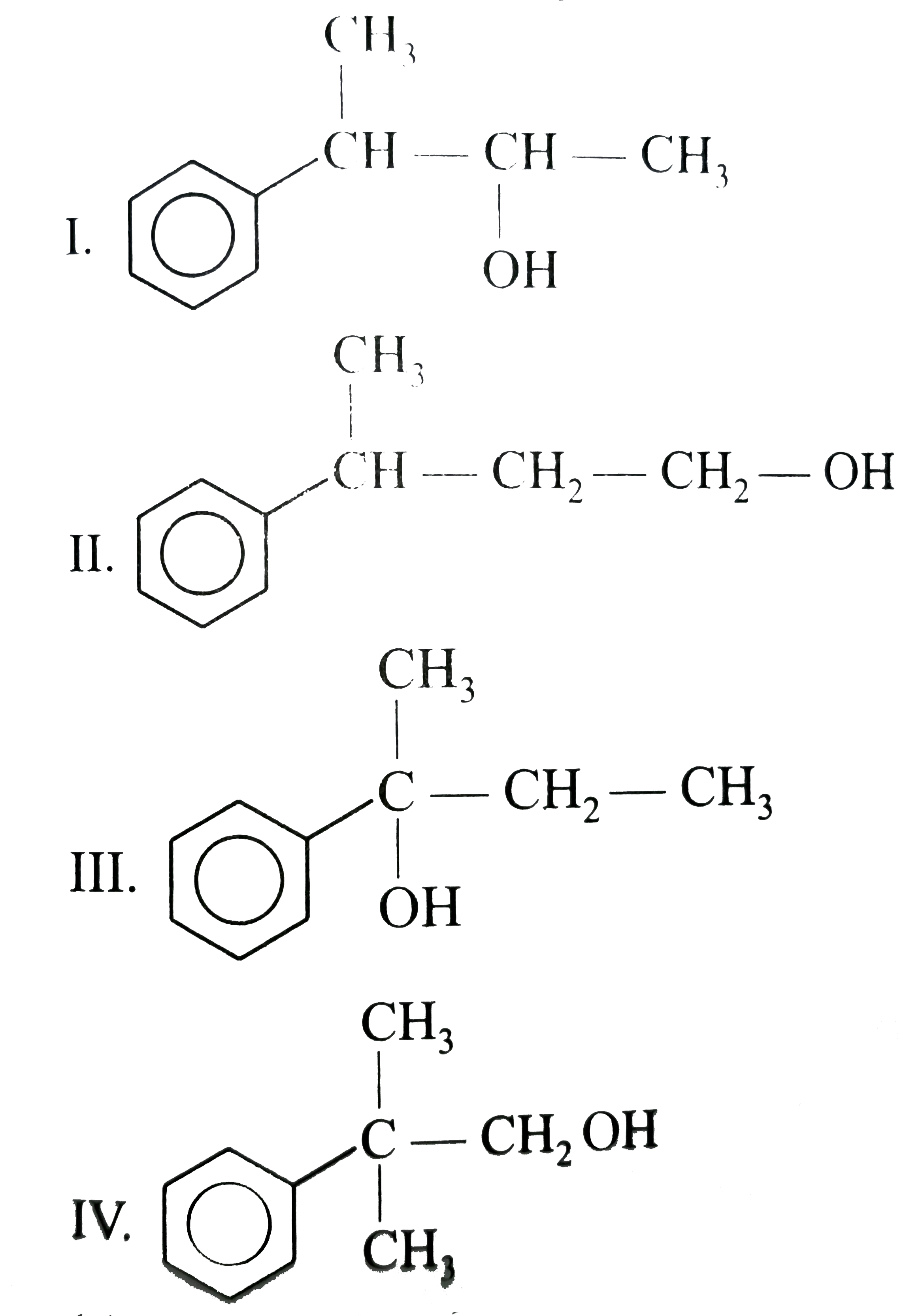
organic chemistry - Yield of possible products from acid catalysed hydration of an alkene with a phenyl group - Chemistry Stack Exchange

SOLVED: Question 13 (1 point) Saved In which of the following reactions can rearrangements occur? a) Acid catalyzed addition of H2O to an alkene Rearrangements occur in reactions (Acid catalyzed addition of